
Solid-State
NMR Applications
 Nuclear
Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is widely used in chemistry for structural
analysis, in molecular biology and the pharmaceutical industry, in material
science, as MRI in clinical diagnostic, in industry.
Nuclear
Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is widely used in chemistry for structural
analysis, in molecular biology and the pharmaceutical industry, in material
science, as MRI in clinical diagnostic, in industry.
High-resolution large-scale version of the poster on the right (NMR applications)
suitable for printing is available free of charge as a .ppt or .pdf file,
please inquire.
Solid-state
NMR spectroscopy has a wide and lasting impact especially on the development
of novel materials: catalysts, battery materials, gas storage materials (fuel
cells) and glasses. All have immediate applications in energy conservation
and the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. In the materials area, developments
in nanotechnology also benefit tremendously from having access to a larger
NMR periodic table than is now routinely available, and the capability to
work with small samples. Another area that benefits greatly is the combinatorial
approach to materials synthesis where the gain in sensitivity (small sample
size) and application of ultra-fast spinning will lead to the rapid evaluation
of new concepts and products. A high-field NMR facility thus allows the greatly
enhanced use of a very powerful and discerning probe of solid-state structure
to a wide range of applications, including:
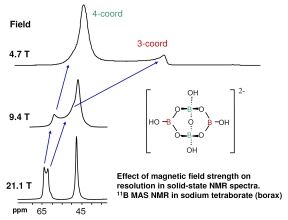 active
sites in catalysts; framework connectivities in catalysts and glasses (structure);
semiconductors, sensors, confined clusters for novel device applications;
interfaces in nanostructured materials and nanocomposites; combinatorial chemistry;
biomolecules, membranes and semisolids via fast spinning; polymers and polymer
blends via fast spinning; dynamics in polymers and biomolecules (small, multiple-labelled
samples); applications in mineral and environmental chemistry
active
sites in catalysts; framework connectivities in catalysts and glasses (structure);
semiconductors, sensors, confined clusters for novel device applications;
interfaces in nanostructured materials and nanocomposites; combinatorial chemistry;
biomolecules, membranes and semisolids via fast spinning; polymers and polymer
blends via fast spinning; dynamics in polymers and biomolecules (small, multiple-labelled
samples); applications in mineral and environmental chemistry
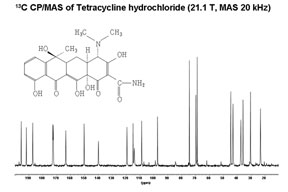 The
new knowledge generated by solid-state NMR is finding many practical and commercial
applications, for example in the petrochemical industry (catalysts, polymers),
alternative energy (battery materials, fuel cells), materials fabrication
(alloys), high tech materials (glasses, ceramics, nanostructured materials),
electronics (novel devices), environmental applications (catalysts, sorbents,
membranes, sensor materials) and pharmaceuticals.
The
new knowledge generated by solid-state NMR is finding many practical and commercial
applications, for example in the petrochemical industry (catalysts, polymers),
alternative energy (battery materials, fuel cells), materials fabrication
(alloys), high tech materials (glasses, ceramics, nanostructured materials),
electronics (novel devices), environmental applications (catalysts, sorbents,
membranes, sensor materials) and pharmaceuticals.